Study Guide
Field 125: Middle Level/Intermediate Mathematics
Sample Selected-Response Questions
Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
General Test Directions
This test contains two sections: (1) a section with selected-response questions and (2) a constructed-response section. The directions for the constructed-response assignment appear before that section.
Each question in the first section is a selected-response question with four answer choices. Read each question and answer choice carefully and choose the start uppercase ONE end uppercase best answer. Try to answer all questions. In general, if you have some knowledge about a question, it is better to try to answer it. You will start uppercase NOT end uppercase be penalized for guessing.
A calculator is available to you for this test. To access the calculator, click on the
icon located in the upper left corner of the screen. A pop-up window containing the calculator will appear. You can reposition the calculator by placing your cursor in the blue area above the calculator and dragging the window to the location of your choice.
Use the numbers on the keyboard and/or point and click with the mouse to enter your computations into the on-screen calculator. When you are finished, close the calculator by clicking the
button in the upper right corner of the calculator.
Reference materials will also be available to you during this test. To access these reference materials, click on the
icon located in the lower left corner of the screen.
You may work on and complete the selected-response questions and the constructed-response assignment in any order that you choose. Be sure to allocate your time carefully so that you are able to complete the entire test within the testing session.
Use of any other type of calculator or outside reference materials during the testing session is prohibited.
Sample Selected-Response Questions
Competency 0001
Apply knowledge of the structure and properties of the real number system.
1. start bold Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows. end bold
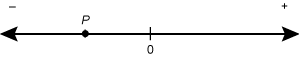 The diagram shows a number line with 0 at the center. The left
end is labeled with a negative sign and the right end is labeled with a positive
sign. Point P is in the middle of the left end.
The diagram shows a number line with 0 at the center. The left
end is labeled with a negative sign and the right end is labeled with a positive
sign. Point P is in the middle of the left end.
Given the location of integer P as shown on the number line, which of the following inequalities is true?
- the square root of P is less than 0
- P to the fourth is less than 0
- 1 over P is greater than 0
- 1 minus P is greater than 0
Correct Response: D. Subtracting an integer P from 1 is equivalent to adding its opposite to 1. Since P is a negative integer based on its location on the number line, the opposite of P is a positive integer. Adding a positive integer to 1 results in a number greater than 0, so 1 minus P greater than 0 must be true.
Competency 0002
Apply knowledge of number operations and number theory.
2. For which of the following does n equals 6 provide a counterexample?
- If n is divisible by 2, then N squared minus 1 is divisible by 5.
- If n is divisible by 3, then N squared minus 1 is divisible by 4.
- If n is divisible by 4, then N squared minus 1 is divisible by 5.
- If n is divisible by 5, then N squared minus 1 is divisible by 4.
Correct Response: B. A counterexample is an example that proves a conditional, or if-then, statement to be false. In other words, it shows that even though the condition of the statement is met, the conclusion is not true. Since 6 is divisible by 3, the condition is met. However, since 6 squared minus 1 is not divisible by 4, the conclusion in response B is false. Thus the statement n equals 6 is a counterexample to the statement in response B.
Competency 0003
Apply the principles and properties of algebraic relations and functions.
3. How does the graph of f left paren x right paren equals left paren x minus a right paren squared plus 2 left paren x minus a right paren minus 6 compare with the graph of g left paren x right paren equals x squared plus 2 x minus 6, given that a is greater than 0?
- The graph of f left paren x right paren is shifted a units to the right.
- The graph of f left paren x right paren is shifted a units to the left.
- The slope of f left paren x right paren is decreased by a units.
- The graph of f left paren x right paren is shifted a units down.
Correct Response: A. Inspection of the two functions shows that f left paren x right paren can be obtained from g left paren x right paren by substituting x minus a for x in g left paren x right paren or f left paren x right paren equals g left paren x minus a right paren. This means that the graph of f left paren x right paren is a horizontal translation of the graph of g left paren x right paren, in this case A units to the right. For example if a equals 3, the graph of f left paren x right paren equals left paren x minus 3 right paren squared plus 2 left paren x minus 3 right paren minus 6 is identical to the graph of g left paren x right paren equals x squared plus 2 x minus 6 shifted to the right 3 units.
Competency 0004
Apply algebraic techniques.
4. start bold Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows. end bold
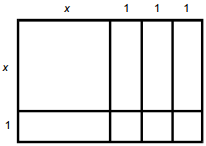 The diagram shows a set of algebra tiles in a
rectangular arrangement. In the upper left is a square tile dimensioned as x by
x units. To the right of the square are 3 rectangular tiles, oriented vertically,
side by side, the same height as the large square, dimensioned as 1 unit wide. Below
the square is a rectangular tile, oriented horizontally, dimensioned as 1 unit high.
At the bottom of each vertical tile and to the right of the horizontal tile are
three square tiles the same dimension as the width of the vertical tiles and the
height of the horizontal tile.
The diagram shows a set of algebra tiles in a
rectangular arrangement. In the upper left is a square tile dimensioned as x by
x units. To the right of the square are 3 rectangular tiles, oriented vertically,
side by side, the same height as the large square, dimensioned as 1 unit wide. Below
the square is a rectangular tile, oriented horizontally, dimensioned as 1 unit high.
At the bottom of each vertical tile and to the right of the horizontal tile are
three square tiles the same dimension as the width of the vertical tiles and the
height of the horizontal tile.
Algebra tiles are arranged as shown in the diagram. This arrangement of algebra tiles could represent which of the following expressions?
- The quantity x plus 1 times the quantity x plus 1 cubed.
- x squared plus 4 x plus 3.
- The quantity x squared plus 3 times the quantity x squared plus 1.
- 2 x squared plus x plus 3.
Correct Response: B. A set of algebra tiles usually consists of large squares that measure x by x, rectangles that measure x by 1, and small unit squares that measure 1 by 1. The area of these squares can be used to represent quadratic expressions since the area of a large square equals x squared the area of a rectangle equals x, and the area of a unit square equals 1. In the diagram given, there are one large square, four rectangles, and three unit squares. Hence, the tiles represent the quadratic expression x squared plus 4 x plus 3 This is also equivalent to left paren x plus 3 right paren left paren x plus 1 right paren, the product of the side lengths of the given figure.
Competency 0006
Apply the properties of quadratic and higher-order polynomial functions and relations.
5. start bold Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows. end bold
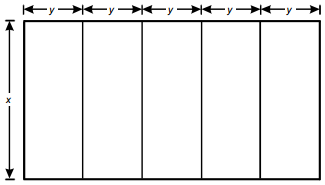 The diagram shows 5 rectangles, oriented vertically, side by side. Their height is dimensioned as x and the width of each is dimensioned as y.
The diagram shows 5 rectangles, oriented vertically, side by side. Their height is dimensioned as x and the width of each is dimensioned as y.
A dog kennel owner plans to build five adjacent rectangular running pens out of 150 meters of fencing. If each pen measures x meters by y meters, with a total area of 468 square meters for the five pens, which of the following quadratic equations can be used to determine the value of x?
- 6 x squared minus 150 x plus 468 equals 0.
- 3 x squared minus 75 x plus 468 equals 0.
- x squared minus 75 x plus 468 equals 0.
- x squared minus 150 x plus 468 equals 0.
Correct Response: B. To build the dog pens as described, the dog kennel owner would need 10 pieces of fencing y meters long (5 pieces for each end) and 6 pieces x meters long. Therefore, 10 y plus 6 x equals 150 Since the total area is the product of the length and the width, 468 equals x times 5 y The first equation is equivalent to 5 y equals 75 minus 3 x. Substituting this equation into the expression for the area results in 468 equals x left paren 75 minus 3 x right paren, which leads to the quadratic equation 3 x squared minus 75 x plus 468 equals 0.
Competency 0007
Apply the principles and properties of radical, rational, absolute value, exponential,
and logarithmic functions.
6. Which of the following verbal descriptions best represents features of the graph of the rational function Y equals the quantity x minus 1 times the quantity x plus 2 times the quantity x plus 3 all over x squared plus 3 x minus 4?
- The graph has a vertical asymptote at x = negative 4 and has 3 x-intercepts.
- The graph has a y-intercept of 1.5 and a hole at x = negative 1.
- The graph has an x-intercept of negative 2 and a vertical asymptote at x = negative 4.
- The graph has a hole at x = 1 and a horizontal asymptote at y = negative 4.
Correct Response: C. Important features of graphs of rational functions are the y-intercept, the x-intercepts, any holes in the graph, and any vertical or horizontal asymptotes. Having the function written so that the numerator and the denominator are both in factored form will help identify these locations. The function y equals the quantity x minus 1 times the quantity x plus 2 times the quantity x plus 3 all over x squared plus 3 x minus 4 equals the quantity x minus 1 times x plus 2 times x plus 3 all over the quantity x minus 1 times the quantity x plus 4.
The x-intercepts occur at the x values that make the numerator zero, but not the denominator zero. The solutions to the quantity x minus 1 times the quantity x plus 2 times the quantity x plus 3 equals 0 are x equals 1, negative 2 or negative 3, but since x equals 1 also makes the denominator zero, the x-intercepts are only at x equals negative 2 and x equals negative 3.
The graph will have a vertical asymptote at the value of x that makes the denominator equal to zero, but not the numerator zero. For this rational function the vertical asymptotes can be found by solving x squared plus 3 x minus 4 equals 0 as follows: x squared plus 3 x minus 4 equals 0
the quantity x plus 4 times the quantity x minus 1 equals 0
x equals negative 4 or x equals 1. The graph of this function will have a vertical asymptote at x equals negative 4 but not at x equals 1 since that will make the numerator also equal to zero. The correct response is C: the graph has an x-intercept of negative 2 and a vertical asymptote at x equals negative 4.
Competency 0010
Apply the principles and properties of Euclidean geometry in two and three dimensions.
7. start bold Use the diagrams below to answer the question that follows. end bold
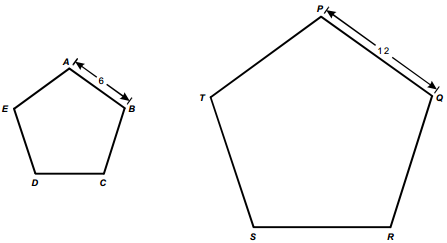 The diagram shows 2 pentagons. One is A B C D E,
and the other is P Q R S T. One side of A B C D E is dimensioned as 6, and one side
of the other is dimensioned as 12.
The diagram shows 2 pentagons. One is A B C D E,
and the other is P Q R S T. One side of A B C D E is dimensioned as 6, and one side
of the other is dimensioned as 12.
If A B C D E is similar to P Q R S T , what is the ratio of the area of A B C D E to the area of P Q R S T ?
- 1 to 9
- 1 to 4
- 1 to 3
- 1 to 2
Correct Response: B. Since A B C D E is similar to P Q R S T corresponding sides of the polygons are proportional. For the polygons in this problem, A B over P Q equals BC over QR equals 1 half. In other words, the length of each side of P Q R S T is twice the length of its corresponding side in A B C D E. The area of A B C D E can be considered to be equal to the sum of N unit squares. The area of P Q R S T is therefore the sum of N squares, with each square having sides of length 2. Since the area of A B C D E is N, the area of P Q R S T is 2 times 2 times N equals 4 N. Hence, the area of A B C D over the area of P Q R S T equals N over 4 N equals 1 fourth.
Competency 0011
Apply the principles and properties of coordinate and transformational geometries.
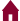
8. When the lines y equals x plus 2, y equals negative 4, and x equals 6 are graphed on a coordinate grid, what is the area of the polygon enclosed by the three lines?
- 8 square units
- 32 square units
- 72 square units
- 144 square units
Correct Response: C. The first step is to graph the three lines on a coordinate grid. graphic, a cartesian graph. The graph shows the 3 lines plotted on a Cartesian graph. Each line is labeled with its equation. Y equals negative 4 is horizontal, 4 units below the x axis. X equals 6 is vertical, 6 units to the right of the y axis. Y equals x plus 2 extends from the lower left quadrant to the upper right quadrant, intersecting y equals negative 4 at an x value of negative 6 and intersecting x equals 6 at a y value of 8. The polygon enclosed is a triangle with a base of 12 units and a height of 12 units. Since the area of a triangle is 1 half b h, the area of this triangle is 1 half times 12 times 12 equals 72 square units.
Competency 0012
Apply the principles, properties, and techniques of probability.
9. start bold Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows. end bold
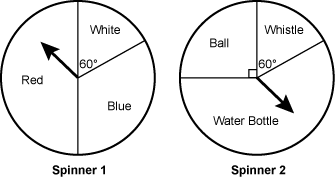 The diagram shows 2 spinners, labeled Spinner 1
and Spinner 2. Spinner 1 is divided into 3 sections, labeled Red, White, and Blue.
The Red section is half of the circle. The interior angle of the White section is
dimensioned as 60 degrees. Spinner 2 is divided into 3 sections, labeled Ball, Whistle,
and Water Bottle. The interior angle of the Ball section is marked as a right angle.
The interior angle of the Whistle section is dimensioned as 60 degrees.
The diagram shows 2 spinners, labeled Spinner 1
and Spinner 2. Spinner 1 is divided into 3 sections, labeled Red, White, and Blue.
The Red section is half of the circle. The interior angle of the White section is
dimensioned as 60 degrees. Spinner 2 is divided into 3 sections, labeled Ball, Whistle,
and Water Bottle. The interior angle of the Ball section is marked as a right angle.
The interior angle of the Whistle section is dimensioned as 60 degrees.
Winners of a game get one spin on each of the two spinners shown to determine what prize they will receive. What is the probability the winner will receive either a white ball or a blue whistle?
- 1 over 432
- 5 over 24
- 7 over 72
- 11 over 12
Correct Response: C. The probability of spinning white on the first spinner is 60 over 360 equals 1 over 6. The probability of spinning a ball on the second spinner is 90 over 360 equals 1 over 4. The probability of winning a white ball is 1 over 6 times 1 over 4 equals 1 over 24. The probability of spinning blue on the first spinner is 120 over 360 equals 1 over 3. The probability of spinning a whistle on the second spinner is 60 over 360 equals 1 over 6. The probability of winning a blue whistle is 1 over 3 times 1 over 6 equals 1 over 18. The probability of winning either a white ball or a blue whistle is 1 over 24 plus 1 over 18 equals 3 over 72 plus 4 over 72 equals 7 over 72.
Competency 0014
Apply the principles of discrete mathematics.
10. start bold Use the matrix definitions below to answer the question that follows. end bold
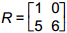
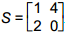
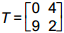
According to the principles of matrix operations, which of the following must be true?
- R open paren ST close paren equals open paren RS close paren T
- RS equals SR
- R to the negative 1 equals 1 over R
- open paren RS close paren to the T equals R to the T S to the T
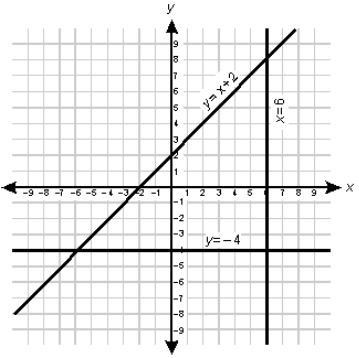
Correct Response: A. This is the associative law for multiplication as applied to matrices. S T equals matrix 1 4, 2 0 times matrix 0 4, 9 2 equals matrix 36 12, 0 8, so R open paren S T close paren equals matrix 1 0, 5 6 times matrix 36 12, 0 8 equals matrix 36 12, 180 108, and R S equals matrix 1 0, 5 6 times matrix 1 4, 2 0 equals matrix 1 4, 17 20, so open paren R S close paren T equals matrix 1 4, 17 20 times matrix 0 4, 9 2 equals matrix 36 12, 180 108. Thus R open paren S T close paren equals open paren R S close paren T equals matrix 36 12, 180 108.
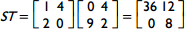 ,
so
,
so
 ,
and
,
and
 ,
so
,
so
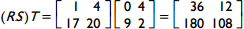 .
Thus,
.
Thus,
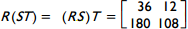 .
.