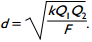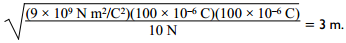Study Guide
Field 013: Physical Science
Sample Selected-Response Questions
Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
General Test Directions
This test consists of two sections: 1) a section with selected-response questions and 2) a constructed-response section.
Each question in the first section is a selected-response question with four answer choices. Read each question and answer choice carefully and choose the start uppercase ONE end uppercase best answer.
Try to answer all questions. Even if you are unsure of an answer, it is better to guess than not to answer a question at all. You will start uppercase NOT end uppercase be penalized for guessing.
The second section of this test consists of one constructed-response assignment. You will be asked to provide a written response to the assignment. Directions for completing your written response to the constructed-response assignment appear immediately before the assignment.
Reference materials will be available to you during this test. To access these reference materials, click on the
icon located in the lower left corner of the screen.
You may start uppercase NOT end uppercase use any type of calculator or outside reference materials during this testing session.
Sample Selected-Response Questions
start bold Use the graph and information below to answer the two questions that follow. end bold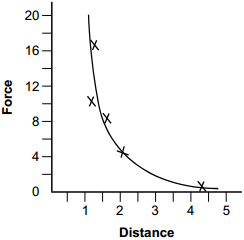
The vertical axis of the graph is labeled Force, with values marked from 0 to 20 in increments of 2. The horizontal axis is labeled Distance, with values marked from 0 to 5 in increments of 1. Each data point is marked with an X at the following approximate values. Force 16.5 at distance 1.25. Force 10 at distance 1.2. Force 8.25 at distance 1.6. Force 4.5 at distance 2. Force 0.5 at distance 4.2. A smooth curve has been drawn that passes through or near all the points.
A physicist has empirically determined the values given on the graph above and drawn a smooth curve to fit the data.
Competency 0004
Understand principles of measurement and the process of gathering, organizing, reporting,
and interpreting scientific data.
1. The physicist was most likely working on a project involving:
- automobile test crashes.
- electrically charged objects.
- the compression of a spring.
- the impact of objects dropped from heights.
Correct Response: B. As the distance between electrically charged objects is increased, the force they exert upon one another decreases. This characteristic is consistent with the data presented in the graph.
Competency 0009
Understand the concepts of energy, work, and power, and the principles of conservation
of energy and momentum.
2. The physicist would like to use the graph to determine how much work is required to move an object from a distance of 1 unit to a distance of 3 units. If d equals distance, which of the following steps should be an important part of the physicist's strategy?
- finding the slope of the curve between D equals 1 and D equals 3
- finding the area under the curve between D equals 1 and D equals 3
- finding the average of the plotted values between D equals 1 and D equals 3
- finding the midpoint of the curve between D equals 1 and D equals 3
Correct Response: B. If the force is constant, the work required to move an object a given distance is the product of the applied force and the distance the object travels. In the graph, the force is not constant, but varies with distance. If the force varies with distance, the force can be assumed to be constant over small increments of distance and the product of the force and the incremental distance can be calculated. Adding these products together results in a value for the work that is equivalent to the area under the force versus distance curve.
Competency 0010
Understand electric charge, electric fields, and electric potential.
3. Two 100 μC charges are located so that they exert an attractive force of 10 N on each other. What is the distance of separation? ( K equals 9 times 10 to the 9 N m squared over C squared. )
-
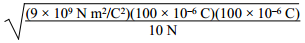 the square root of the quantity 9 times 10 to the 9 N
m squared over C squared times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6 C times
the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6 C all over 10N.
the square root of the quantity 9 times 10 to the 9 N
m squared over C squared times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6 C times
the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6 C all over 10N. -
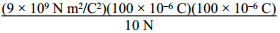 the quantity 9 times 10 to the 9 N m squared over
C squared times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6 C times the quantity
100 times 10 to the negative 6 C all over 10N.
the quantity 9 times 10 to the 9 N m squared over
C squared times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6 C times the quantity
100 times 10 to the negative 6 C all over 10N. -
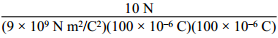 10N over the quantity 9 times 10 to the 9 N m squared
over C squared times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6, C times the quantity
100 times 10 to the negative 6 C.
10N over the quantity 9 times 10 to the 9 N m squared
over C squared times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6, C times the quantity
100 times 10 to the negative 6 C. -
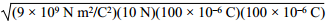 the square root of the quantity 9 times 10 to the
9 N m squared over C squared times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6,
C times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6 C.
the square root of the quantity 9 times 10 to the
9 N m squared over C squared times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6,
C times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6 C.
Correct Response: A. Coulomb's law states that the force between two charges is directly proportional to the constant left paren start italics k end italics right paren and the product of the two charges and is inversely proportional to the square of the distance of separation, which is given by F equals k Q sub 1 Q sub 1 over d squared. Solving this equation for distance left paren start italics d end italics right paren gives d equals the square root of k Q sub 1 Q sub 2 over F. Substituting the values from the question, d equals the square root of the quantity 9 times 10 to the 9 N m squared over C squared times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6 C times the quantity 100 times 10 to the negative 6 C all over 10N equals 3 meters.
Competency 0012
Understand magnetic fields and electromagnetic induction.
4. An alternating-current-carrying wire induces a current in another nearby wire. This phenomenon is the basis for the operation of which of the following devices?
- motor
- generator
- galvanometer
- transformer
Correct Response: D. As the magnetic lines of force left paren flux lines right paren build up and collapse with the changes in current passing through one coil, current is induced in another coil. This process, known as electromagnetic induction, is the basis for the operation of transformers, which are used to either increase or decrease voltages in electrical systems.
Competency 0014
Understand the characteristics of sound waves and electromagnetic waves (including
light and optics).
5. start bold Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows. end bold
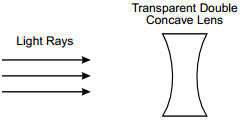
The diagram shows the cross-section of a lens, labeled Transparent Double Concave Lens. Three parallel arrows, labeled Light Rays, travel horizontally toward the lens from the left.
Which of the following responses correctly traces the path of parallel light rays as they travel from the light source and encounter the lens shown in the diagram?
-
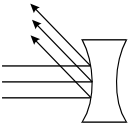 The rays strike the left surface of the lens and are reflected
in parallel up to the left.
The rays strike the left surface of the lens and are reflected
in parallel up to the left.
-
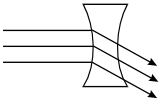 The rays pass into the lens, As they enter the lens, they bend
downward. They exit straight through the right surface, traveling in parallel downward
to the right.
The rays pass into the lens, As they enter the lens, they bend
downward. They exit straight through the right surface, traveling in parallel downward
to the right.
-
 The rays pass into the lens. As they enter the lens, the top
ray bends upward, the middle ray continues horizontally, and the bottom ray bends
downward. As they exit the lens, the top ray bends further upward, the middle ray
continues horizontally, and the bottom ray bends further downward.
The rays pass into the lens. As they enter the lens, the top
ray bends upward, the middle ray continues horizontally, and the bottom ray bends
downward. As they exit the lens, the top ray bends further upward, the middle ray
continues horizontally, and the bottom ray bends further downward.
-
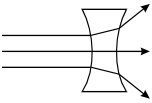
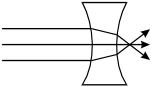 The rays pass into the lens. As they enter the lens, the top
ray bends downward, the middle ray continues horizontally, and the bottom ray bends
upward. As they exit the lens, the top ray bends further downward, the middle ray
continues horizontally, and the bottom ray bends further upward, so they all intersect
at a point slightly outside the lens and continue in their respective directions.
The rays pass into the lens. As they enter the lens, the top
ray bends downward, the middle ray continues horizontally, and the bottom ray bends
upward. As they exit the lens, the top ray bends further downward, the middle ray
continues horizontally, and the bottom ray bends further upward, so they all intersect
at a point slightly outside the lens and continue in their respective directions.
Correct Response: C. The speed of light is slower in glass than in air. As light passes from air to glass, its trajectory is bent toward the normal, a line drawn perpendicular to the surface of the lens. As the light exits the glass on the other side of the lens its speed increases, causing its trajectory to be bent away from the normal. Applying this property to the geometry of the double concave lens shows that parallel rays incident on the lens diverge.
Competency 0015
Understand various models of atomic structure and the organization of the periodic
table.
6. start bold Use the graph below to answer the question that follows. end bold
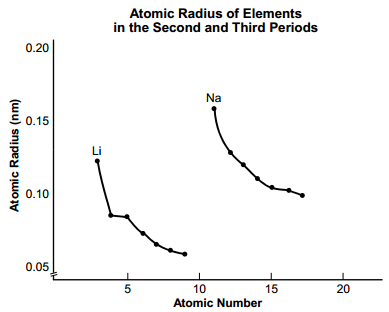
The title of the graph is Atomic Radius of Elements in the Second and Third Periods. The vertical axis is labeled Atomic Radius in mm and has values marked from 0.05 to 0.02 in increments of 0.05. The horizontal axis is labeled Atomic Number and has values marked from 0 to 20 in increments of 5. There are two data curves. The first point of the first curve is labeled Li. The approximate values of the points of this curve are as follows. Atomic number, 3. Atomic Radius, 0.145. Atomic number, 4. Atomic Radius, 0.105. Atomic number, 5. Atomic Radius, 0.085. Atomic number, 6. Atomic Radius, 0.070. Atomic number, 7. Atomic Radius, 0.065. Atomic number, 8. Atomic Radius, 0.60. Atomic number, 9. Atomic Radius, 0.50. The first point of the second curve is labeled Na. The approximate values of the points of this curve are as follows. Atomic number, 11. Atomic Radius, 0.180. Atomic number, 12. Atomic Radius, 0.150. Atomic number, 13. Atomic Radius, 0.125. Atomic number, 14. Atomic Radius, 0.110. Atomic number, 15. Atomic Radius, 0.100. Atomic number, 16. Atomic Radius, 0.100. Atomic number, 17. Atomic Radius, 0.100.
The graph shows the relationship between atomic radius and atomic number for elements in the second and third periods of the periodic table. According to the graph, which of the following statements are true?
- Roman numeral 1. Within a group, atomic radius tends to decrease as atomic number increases.
- Roman numeral 2. Within a period, atomic radius tends to decrease as atomic number increases.
- Roman numeral 3. The largest element in the fourth period is expected to be potassium.
- Roman numeral 4. Within a period, main group metals tend to be smaller than nonmetals.
- roman numeral 1 and roman numeral 3 only
- roman numeral 1 and roman numeral 4 only
- roman numeral 2 and roman numeral 3 only
- roman numeral 3 and roman numeral 4 only
Correct Response: C.
In each curve on the graph, the atomic number is increasing in increments of one
as the atomic radius decreases. This indicates that each curve represents a period
of the periodic table. The second period starts with lithium (L i), which has the
largest atomic radius of the elements in the second period. The third period starts
with sodium (N a), which has the largest atomic radius of the elements in the third
period. Given this trend in the periodic table, the fourth period should start with
potassium (K), which will have the largest atomic radius of the elements in the
fourth period.
Competency 0016
Understand the physical and chemical properties of matter and the types of bonds
between atoms.
7. Which of the following properties is most likely to be associated with nonpolar covalent substances?
- high freezing point
- good electrical conduction
- high boiling point
- poor thermal conduction
Correct Response:D. Molecules held together by covalent molecular bonds are formed by the sharing of electrons. In a nonpolar molecule, the electrons are shared equally between the bonding atoms. This equal sharing causes the forces between the molecules of a nonpolar covalent substance to be relatively weak. Weak intermolecular forces result in the poor conduction of thermal energy—the energy of molecular motion—through the substance.
Competency 0017
Understand the relationship between the mole concept, chemical formulas, and chemical
equations.
8. start bold Use the reaction below to answer the question that follows. end bold
2 C sub 8 H sub 18 plus 25 O sub 2 yields chemical reaction symbol 16 C O sub 2 plus 18 H sub 2 O
The chemical equation shown represents the combustion of octane, a component of gasoline. If 114 grams of octane are burned in the presence of excess oxygen, how many grams of carbon dioxide will be produced?
- 44 grams
- 176 grams
- 352 grams
- 912 grams
Correct Response: C. The coefficients of the chemical equation state that for every 2 moles of octane consumed, 16 moles of carbon dioxide will be produced. Since 1 mole of octane has a mass of 8 right paren 12 grams right paren plus 18 left paren 1 grams right paren equals 114 grams 1 mole of octane is combining with oxygen and will therefore produce 8 moles of carbon dioxide. The mass of 8 moles of carbon dioxide is 8 left square bracket left paren 12 grams right paren plus 2 left paren 16 grams right paren right bracket equals 352 grams.
Competency 0020
Understand chemical reactions, reaction rates, and chemical equilibrium.
9. start bold Use the graph below to answer the question that follows. end bold
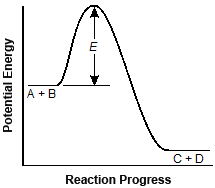
The horizontal axis of the graph is labeled Reaction Progress, and the vertical axis is labeled Potential Energy. No units are marked. The data curve starts about halfway up the vertical axis with a short horizontal segment labeled A plus B. The curve then rises steeply and makes a sharp, smooth turn downward into a steep slope to a horizontal segment near the horizontal axis, labeled C plus D. The vertical distance from the A plus B segment to the peak of the upper crest is dimensioned as E.
The graph shows the activation energy (E) for the following reaction:
A plus B yields C plus D.
Which of the following graphs will result if a catalyst is added to the reactants?
Each response is the same graph with one or two differences.
-
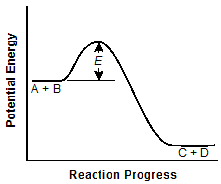 The vertical distance E is about half that in
the original graph.
The vertical distance E is about half that in
the original graph. -
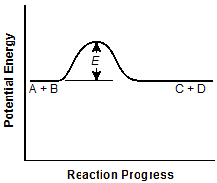 The vertical distance E is about half that in
the original graph, and the C plus D horizontal segment is at the same level as the
A plus B segment.
The vertical distance E is about half that in
the original graph, and the C plus D horizontal segment is at the same level as the
A plus B segment. -
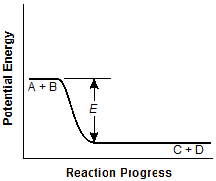 The curve falls from the A plus B segment to the
C plus D segment without a peak in between. The dimension E now measures the vertical
distance from the A plus B segment to the D plus D segment, and it is about three fourths
the measure of that in the original graph.
The curve falls from the A plus B segment to the
C plus D segment without a peak in between. The dimension E now measures the vertical
distance from the A plus B segment to the D plus D segment, and it is about three fourths
the measure of that in the original graph. -
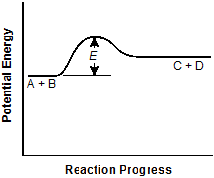 The vertical distance E is about half that in
the original graph, and the C plus D segment is now vertically about halfway between
the A plus B segment and the peak of the curve.
The vertical distance E is about half that in
the original graph, and the C plus D segment is now vertically about halfway between
the A plus B segment and the peak of the curve.
Correct Response: A. A catalyst increases the reaction rate of a chemical reaction's progress without altering the chemical properties of the reactants or the products. It does this by lowering the activation energy of the reaction. This is reflected in graph A.
Competency 0021
Understand the properties of solutions and the theories, principles, and applications
of acid-base chemistry.
10. The reaction of a strong acid with a carbonate will result in the formation of a salt plus which of the following?
- C O sub 2 plus H sub 2 O
- C O plus H sub 2 O
- C O sub 2 plus H sub 2 O sub 2
- C O plus H sub 2
Correct Response: A. When a strong acid reacts with a carbonate, a salt plus carbon dioxide and water are produced. In such a reaction, the acid donates two hydrogen ions (H sup plus) to the carbonate ion (C O sub 3 sup 2 minus) to produce carbonic acid (H sub 2 C O sub 3), which is a weak acid. Carbonic acid, which is unstable, rapidly decomposes into water (H sub 2 O) and carbon dioxide (C O sub 2). An example of this type of reaction is that between sulfuric acid and sodium carbonate as shown below. H sub 2 S O sub 4 plus N a sub 2 C O sub 3 yields N a sub 2 S O sub 4 plus H sub 4 C O sub 3 yields N a sub 2 S O sub 4 plus H sub 2 O plus C O sub 2